Accurate audience targeting is key to campaign success. But it can be tricky to navigate. Even with buyer personas, there are lots of options and nuances to consider when creating audiences. This article is for agencies and advertisers looking to take audience targeting past the basics. We’ll explore a range of targeting techniques and give you actionable tips for your next campaigns.
The Fundamentals of LinkedIn Audience Targeting
LinkedIn’s targeting features are unrivaled, leveraging various audience attributes to ensure precise ad delivery. And with over 1 billion members, advertisers can reach people based on job titles, industry, company size, skills, and interests. It means you can:
- Tailor ads to resonate with professional needs and challenges
- Create messaging that speaks to your audience’s interests
- Reduce wasted ad spend and focus on the most relevant audience segments
LinkedIn Ads audience allows advertisers to refine their audience using various attributes such as demographics, job experience, and member interests, enabling the creation of custom audience segments for more effective targeting.
Defining Your Target Audience
Defining your target audience is a crucial step in creating effective LinkedIn ads. It involves identifying the characteristics, behaviors, and interests of your ideal audience. By understanding your target audience, you can create ads that resonate with them, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
To define your target audience, consider the following factors:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, job title, industry, and company size. These basic attributes help you narrow down who might be interested in your product or service.
- Interests and Traits: Member interests, skills, and traits that align with your product or service. For instance, if you’re marketing a project management tool, targeting members with project management skills or interests can be highly effective.
- Behaviors: Job functions, seniority, and experience that indicate a need for your product or service. For example, targeting senior IT professionals for a cybersecurity solution.
- Company Attributes: Company industry, size, and connections that align with your target audience. If your product is tailored for large enterprises, targeting companies with over 500 employees in specific industries can be beneficial.
By considering these factors, you can create a comprehensive profile of your target audience and tailor your LinkedIn ads to effectively reach and engage with them.
Basic Segmentation Strategies
LinkedIn offers basic segmentation options which should be self explanatory, but let’s take a look.
- Demographic Targeting: Age, Gender, Location
Location targeting is a no brainer and there’s a reason why it’s a mandatory field. It’s determined by location specified on the user’s profile but also the IP address. Unless you’re running a retargeting campaign, switch location targeting to permanent.
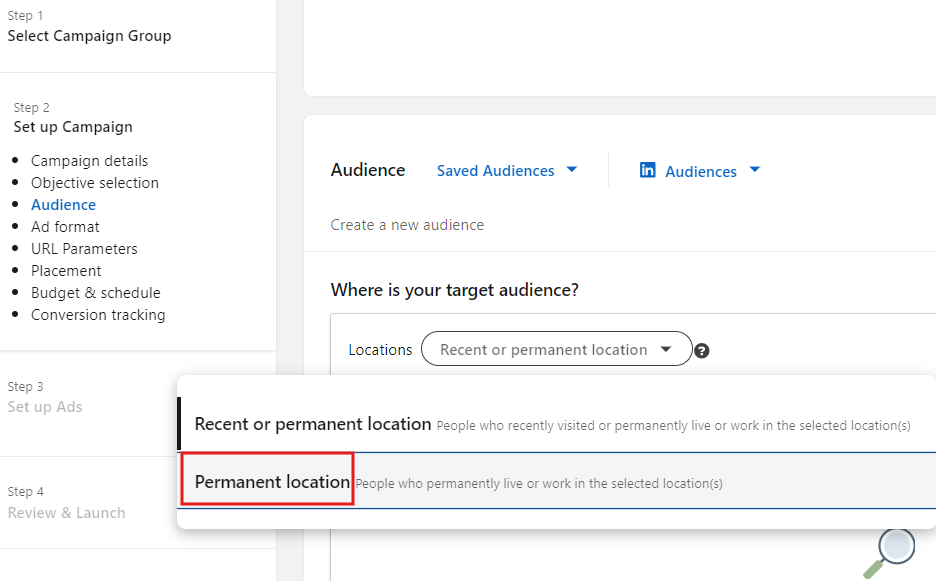
Age is an estimation based on graduation year and not everyone enters a graduation year. We’d recommend using Years of Experience or seniority over age.
Gender is assumed, based on a member’s name. LinkedIn doesn’t require members to enter gender and we typically wouldn’t recommend using it to target. However, ‘member gender’ can be useful in building precise audience profiles based on inferred user information, which is crucial for effectively reaching specific demographics in advertising campaigns.
- Job Functions
Job functions are a standardized grouping of titles, for example, digital marketing manager, social media analyst and CMO would all sit under the Marketing job function. Whether you’re targeting software engineers or HR professionals, targeting by job function means you’re not missing job titles.
Top Tip: Combine Job Function with Seniority to reach decision makers.
- Industry
Targeting industries means you can ensure messaging speaks directly to the unique challenges of those sectors.
Note though, don’t assume that a specific company sits under an obvious industry – for example a device manufacturer may sit under healthcare or medical equipment manufacturing. Have a look at a few company pages on your target account list to see how they categorize themselves.
- Educational Background Segmentation
Targeting by educational background can be useful if your offer appeals to a certain level of education or specific schools, colleges or universities. Be aware, this information is not required when creating a profile so you could be missing out on relevant people. The audience estimation will give you an indication of whether you’ll reach enough people. Additionally, targeting ‘member schools’ can refine demographic targeting by specifying the educational background of potential audience members, leading to more relevant engagements.
- Geographical and Language Segmentation
Targeting by geography and language is key to global or multilingual campaigns. Think about local customs, trends and market conditions that may influence messaging. And if you’re targeting a multilingual audience, crafting ads in their preferred language can boost engagement.
Advanced Targeting Techniques on LinkedIn
So we’ve covered the basics, but how can we go deeper to really focus our audience?
One advanced technique is interest targeting, which integrates data from search engines like Bing and professional platforms such as LinkedIn to define and reach an ideal audience by leveraging user interests and behaviors. Additionally, company connections allow marketers to target the 1st-degree connections of employees at specific companies, particularly those with over 500 employees, enhancing the effectiveness of B2B marketing campaigns.
Exploring Detailed Interests and Traits Targeting Options
Options like skills groups and company size mean we can fine-tune targeting to get as close to our ideal customer profile (ICP) as possible. Skills targeting is useful because it means you can target people with a specialized expertise that may not be called out in a job title.
For example, if your business sells a SaaS ERP tool, Job Title targeting may be more generic – IT manager, director, IT operations analyst. But using skills allows you to target specific competencies, and in this case, SaaS, ERP etc, that may span a range of job titles.
Location and Language Targeting
Location and language targeting are essential components of LinkedIn ads targeting. By targeting specific locations and languages, you can ensure that your ads are seen by the right people in the right regions.
- Location Targeting: Target specific countries, states, cities, or metropolitan areas to reach your ideal audience. For instance, if your service is only available in North America, you can focus your ads on the United States and Canada.
- Language Targeting: Target specific languages to reach your ideal audience, including English, Spanish, French, and more. This ensures that your message is understood and resonates with the audience.
To optimize your location and language targeting, consider the following best practices:
- Use location targeting to reach specific regions or countries where your product or service is most relevant. For example, a financial service might target major financial hubs like New York, London, and Tokyo.
- Use language targeting to reach specific languages that align with your target audience’s native language. Crafting ads in the audience’s preferred language can significantly boost engagement.
- Use a combination of location and language targeting to reach a specific audience, such as Spanish-speaking professionals in the United States. This dual approach ensures your ads are both geographically and linguistically relevant.
Interests and Traits Targeting
Interests and traits targeting allow you to target specific member interests and traits that align with your product or service. By targeting these interests and traits, you can increase the relevance of your ads and improve conversion rates.
- Interests Targeting: Target specific member interests, such as hobbies, passions, or industries. For example, if you’re promoting a new marketing tool, you might target members interested in digital marketing, content creation, or social media.
- Traits Targeting: Target specific member traits, such as skills, certifications, or experience. This could include targeting members with certifications in project management or those with extensive experience in software development.
To optimize your interests and traits targeting, consider the following best practices:
- Use interests targeting to reach specific audiences that align with your product or service, such as professionals interested in marketing or finance. This ensures your ads are relevant to their professional interests.
- Use traits targeting to reach specific audiences that align with your product or service, such as professionals with specific skills or certifications. For instance, targeting members with a certification in digital marketing if you’re offering a new marketing tool.
- Use a combination of interests and traits targeting to reach a specific audience, such as professionals interested in marketing with a certification in digital marketing. This layered approach can significantly enhance ad relevance and engagement.
The Significance of Retargeting
Retargeting is great for reconnecting with people who’ve interacted with your brand but didn’t convert. By serving ads to people who engaged with your content, you keep your brand top-of-mind. You’re gently nudging them toward conversion! Campaign Manager makes it easy to set up multiple audiences to retarget:
- People who viewed over 50% of a video ad
- People who visited a specific page on your website
- People who opened a lead generation form but didn’t complete it
Utilizing Predictive and Matched Audiences
Predictive Audiences is exactly that – it uses AI to predict which users will likely convert by analyzing patterns in your data sources – contact lists, lead forms, conversions. It then builds you an audience to use in campaigns. You’ll need to upload at least 300 contacts, so that LinkedIn’s machine learning can do its thing.
We prefer using Matched audiences, especially if you have a list of companies or contacts you want to reach. You can upload this data and build audiences using the exact audience you want to go after. Leveraging best practices for LinkedIn ads, such as refining targeting based on demographics, job experience, and member interests, can significantly enhance ad delivery and engagement.
Implementing ABM on LinkedIn
The best ABM campaigns are the ones that create personalized, high-impact interactions that resonate. You can carve out broader ABM campaigns to talk to a given industry or job function, or you can get super granular and target individual companies.
Integrating LinkedIn Audience Targeting into Your Campaigns
With all the targeting options available, what practical ways can you implement this information into your campaigns? Understanding the target audience size is crucial for determining effective targeting options for advertisements. Additionally, reaching the right audience is essential for the success of LinkedIn ad campaigns, as a well-defined audience can lead to better conversion rates. Let’s take a look…
Aligning Ad Content with Audience Segments
If your ad content doesn’t resonate with your audience, your campaign will fail. Simple as that. Different segments respond to different messaging, so create your ads based on their unique needs, interests and pain points.
For example, a tech crowd might appreciate content that goes a bit deeper with the tech benefits, while a business unit might respond better to user-friendly benefits.
The key is to make ads feel personalized and relevant. In fact, the best ads don’t even look like ads.
Dynamic Ad Personalization
Dynamic ad personalization is a game-changer for LinkedIn campaigns. It uses audience profile data to serve customized ads.
Message, conversation and dynamic ad formats (follower, spotlight and job) all allow you to use macros to personalize copy.
Testing and Optimizing Target Audiences
Effective audience targeting isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it strategy. And you’ve heard it before but test, test and test again! Use A/B testing to compare how different segments respond to messages or creatives, and monitor performance metrics to identify which audiences are delivering the best results.
Audience Size and Optimization
Audience size and optimization are critical components of LinkedIn ads targeting. By optimizing your audience size, you can ensure that your ads are seen by the right people and improve conversion rates.
- Audience Size: Target a specific audience size, such as 10,000 to 100,000 professionals. This range ensures your ads reach a substantial number of potential leads without being too broad.
- Optimization: Use LinkedIn’s optimization algorithms to optimize your audience size and targeting. These tools help you refine your audience to those most likely to engage with your ads.
To optimize your audience size and targeting, consider the following best practices:
- Use a minimum audience size of 300,000 for sponsored content and 60,000-400,000 for text ads. This ensures your ads have enough reach to gather meaningful data and drive results.
- Use LinkedIn’s optimization algorithms to optimize your audience size and targeting. These algorithms analyze performance data to help you refine your audience for better results.
- Monitor your campaign performance and adjust your audience size and targeting as needed to improve conversion rates. Regularly reviewing performance metrics allows you to make data-driven decisions and optimize your campaigns effectively.
By following these best practices, you can effectively define your target audience, optimize your location and language targeting, interests and traits targeting, and audience size and optimization to improve the performance of your LinkedIn ads.
Measuring Success: KPIs and Metrics
Campaign Manager provides loads of data to help you measure the success of campaigns – click through rate, cost per click, cost per acquisition – you know the score. But are your campaigns actually driving revenue? Go past the basic reporting metrics and consider revenue attribution and return on ad spend to really get the attention of your CMO.
Mastering LinkedIn’s audience targeting techniques, from basic segmentation to advanced strategies like ABM, is key to driving great ad campaigns. But you’ll only know what works once you start testing. Try some of the strategies we’ve discussed in this post and let us know how you get on! Go even further with advanced budget and bid strategies, and set yourself up for success with advanced LinkedIn Ads optimizations.
FAQs: Comprehensive Audience Targeting
Identify your ideal customer profile based on demographics, job titles, industries, and interests that align with your product or service. Use LinkedIn’s audience insights and analytics to refine and validate targeting.
Accordion content.Segment by job function, industry, company size or seniority level to tailor your messaging. Use LinkedIn’s advanced targeting options like skills, groups, and company followers to reach specific professional audiences.
You should be reviewing and checking in on campaigns often to gauge success. Performance metrics like click through rate will give you an idea of whether ads are working with the audience targeting you’ve specified. Adjust targeting based on campaign goals, market changes and audience behavior shifts to optimize effectiveness.
Segment by job function, industry, company size or seniority level to tailor your messaging. Use LinkedIn’s advanced targeting options like skills, groups, and company followers to reach specific professional audiences.dion content.
You should be reviewing and checking in on campaigns often to gauge success. Performance metrics like click through rate will give you an idea of whether ads are working with the audience targeting you’ve specified. Adjust targeting based on campaign goals, market changes and audience behavior shifts to optimize effectiveness.ent.
Precise audience targeting improves ad relevance and engagement, leading to higher CTRs, lower CPCs, and increased conversion rates. It maximizes ROI by ensuring your ads reach those most likely to convert.
Avoid broad targeting that dilutes ad relevance, but also avoid hyper-targeting. It’s tempting to use every targeting feature going but you’ll end up with a tiny audience and a campaign that simply doesn’t get traction.
